Diamond Evaluation
We buy diamond jewelry (every diamond size), loose diamonds (0.50+ carat), and even damaged diamonds (1.0+ carat). Our diamond department is very well equipped with the latest technology and experts able to work on any diamond. We also have two top-notch machines (GIA iD100 and GIA DiamondCheck) to support our experts during the grading process.
Handling Time
Turnaround time for up to 0.75 carat: 1 business day
Turnaround time for 0.75 carat to 2.00 carats: 2 business days
Turnaround time for 2.00+ carats: 3 business days
How Diamond Evaluation Works
We have established a multi-point inspection for diamonds.
Weight > Color > Clarity > Cut > Shape
Diamond Weight
Yes, the weight matters, but a smaller stone can easily outvalue a bigger stone depending on other factors.
Diamond Color
A diamond’s color is truly important. Diamond color ranges from D to Z.
Diamond Clarity
Diamond clarity ranges from FL (flawless) to I3 (obviously included).
Diamond Shape
The shape of a diamond matters a lot. Some shapes, like round diamonds, may always be in demand, while others, like the pear shape, may go out of fashion.
Diamond Cut
The cut influences even the clarity of a diamond. An excellent cut from rough material is highly desirable.
Fluorescence
Fluorescence can have a significant effect on a diamond’s value. Especially high-grade stones like D, E, and F can be negatively impacted.
Diamond Origin
A diamond’s origin is interesting but usually subservient to a stone’s value.
Symmetry
Symmetry is very important. An uneven-looking stone is less desirable.
Grading Report
A GIA grading report is very helpful when marketing a diamond.
We are very happy to appraise your diamonds. Our purchase offer will be highly competitive, and there is no obligation to sell your diamond to us.
How To Appraise A Diamond
reDollar.com is very transparent when it comes to sell a diamond. We will always provide you with a detailed laboratory report explaining how we appraised your diamond and how we calculated your purchase offer. Learn more about the diamond appraisal process and the 4 C’s that will be responsible for the value of your diamond.
(Natural mined) diamonds are one of the most sought-after and valuable gemstones in the world. Many people are interested in understanding how appraisinga diamond works. An understanding of the process and criteria included in performing a diamond appraisal can help a consumer make a decisions when it comes to buying or selling those precious gemstones. With that in mind, here is a closer look at how appraising a diamond works and what is typically taken into account.
The 4 C’s of a Diamond Appraisal
The first step in appraising a diamond is to evaluate accordingly to the so called 4 C’s: Cut, Clarity, Color, and Carat Weight. These universally accepted characteristics are responsible for the value of a diamond. In addition to 4 C’s, a professional diamond appraiser will look for evidence of treatments or enhancements of the stone that may decrease its value. These treatments include any heating, laser drilling, or coating processes that may affect the color, clarity, and durability of the stone.
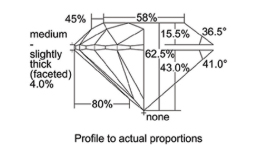
A Diamond’s Cut
The cut is one of the primary contribution of a diamond’s beauty and sparkle. The rating of the cut is evaluated according to its proportions, symmetry, and finish quality. Different cuts can create different optical effects and even alter the apparent size of the diamond. It is important to understand which cut will best showcase the a specific diamond in a specific type of jewelry and setting.
Diamond’s Cut Scale
(1) excellent cut (2) very good cut (3) good cut (4) fair cut (5) poor cut
A Diamond’s Clarity
Clarity is another important factor. Diamonds have internal flaws and blemishes, and the clearer they are, the more valuable they become. The clarity is assigned based on the degree of the flaws present in the diamond. Flaws such as clouds, feathers, and pins can be seen under a loupe or microscope. The industry standard for grading a diamond is a 10 power magnification of the gemstone.
A Diamond’s Clarity Scale
(1) Flawless (2) Internally Flawless (3) VVS1 (4) VVS2 (5)VS1 (6) VS2 (7) SI1 (8) SI2 (9) I1 (10) I2 (11) I3
A Diamond’s Color
Color is also an important factor in determining the value of a diamond. Most diamonds appear to be clear with a hint of yellow or grey, but some diamonds can have a higher saturation of color, such as those that are yellow, pink, blue, or green. The more intense the color, the more valuable the diamond. Natural colored diamonds are also called “fancy diamonds” and belong to the most valuable gemstones in the world.
A Diamond’s Color Scale
Colorless Diamonds (D, E, F); Near Colorless Diamonds (G, H, I, J); Faint (K, L, M); Very Light Colored Diamonds (N, O, P, Q, R); Light Colored Diamonds (S, T, U, V, W, X, Y, Z)
A Diamond’s Carat Weight
The final C of the four C’s is carat weight, which refers to the weight of the diamond. The higher the carat weight, the more valuable the stone can be. A smaller diamond having overall better characteristics than a heavier diamond may be more valuable. The carat weight is one characteristic of the 4 Cs and appraising a diamond’s value is literally impossible without evaluating the cut, the color, and the clarity. Don’t get fooled by the carat weight: some jewelry chains use the carat weight as THE ULTIMATE selling point.
Understanding Carat Weight
1 carat = 0.20 gram = 0.128603 pennyweight

Colored diamonds can also be appraised and valued in the same manner. In addition to the 4 C’s, however, it is important to evaluate the intensity and hue of the color. The more intense the color, the more expensive the stone is. Hue refers to the actual color tone, such as pink, yellow, or green, while the intensity is the strength or depth of the hue.
(!) reDollar.com is always a buyer for fancy diamonds. We have the financial means to buy highly valuable diamonds.
Lab Created Diamonds
It is important to note that lab created diamonds have very little value when compared to natural mined diamonds. Since they are created in a manufactured environment with full control of the properties of the diamond, it is much easier to create a higher quality diamond than it is to find a natural diamond with these same characteristics. Therefore, lab created diamonds will usually have very little value.
The Importance of Professional Appraisal
When appraising a diamond, it is important to use a professional gemologist in order to accurately assess the value of the stone. A professional gemologist will have the knowledge and experience needed to correctly evaluate the present diamond according to its Four C’s. a reputable diamond buyer such as reDollar.com will have their own accredited gemologists and will pay top dollar for loose or mounted diamonds. Understanding the appraisal process and methods can help you make better decisions when it comes to sell a loose diamond or diamond jewelry.